Pulmonary hypertension – High blood pressure in the lung
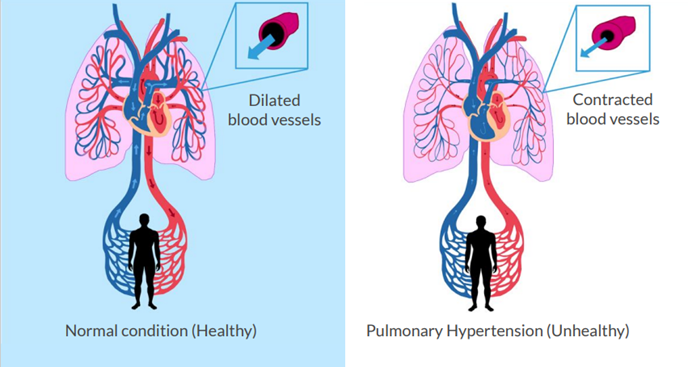
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure in the pulmonary circulation is elevated. It is a potential life-threatening state since it increases the workload and thereby strains the weak right side of the heart which pumps the blood through the lungs to re-oxygenate it. Already at onset, pulmonary hypertension is associated with an acute risk for right heart failure and death.
Pulmonary hypertension should not be confused with “normal” high blood pressure, hypertension. Hypertension is elevated pressure in the blood vessels of the systemic circulation, and it is generated by the work of the left side of the heart, distributing blood throughout the body. Long standing hypertension is associated with increased risk for cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
Pulmonary hypertension can be triggered acutely or develop slowly for several years and can be divided in two larger categories:
Acute pulmonary hypertension which requires immediate intensive care treatment to avoid right-sided heart failure and sudden death.
Chronic pulmonary hypertension which develops slowly over time, is often diagnosed late in the process and which requires daily medication.
Attgeno is currently clinically investigating the role of Supernitro in acute pulmonary hypertension and is pre-clinically exploring Supernitro’s potential for treating chronic pulmonary hypertension.